How Alexander the Great’s Death Shaped His Empire
Alexander the Great rule over all the land
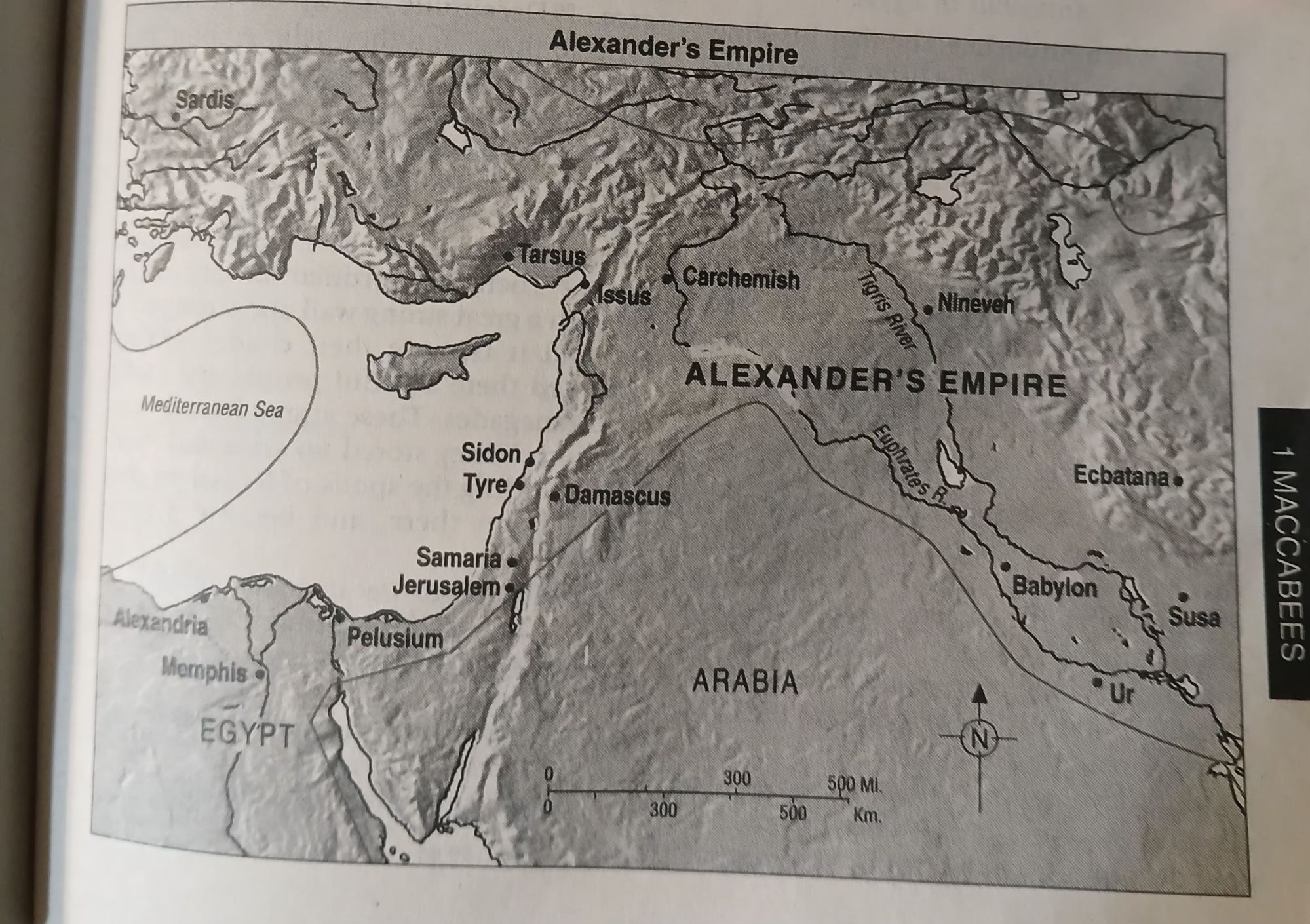
1 Maccabees 1:1-4 After Alexander of Macedon, the son of Philip, had come from the land of Kittim and defeated Darius, the king of the Persians and the Medes, he succeeded him as king, in addition to his position as king of Greece. He engaged in many campaigns, captured strongholds, and executed kings. In his advance to the ends of the earth, he plundered countless nations. When the earth was reduced to silence before him, his heart swelled with pride and arrogance. He recruited a very powerful army, and as provinces, nations, and rulers were conquered by him, they became his tributaries.
After defeating the Persians, Alexander the Great reached the Indian Ocean.
Alexander the Great Dies
1 Maccabees 1:5-9 However, when all this had been accomplished, Alexander became ill, and he realized that his death was imminent. Therefore, he summoned his officers, nobles who had been brought up with him from his youth, and he divided his kingdom among them while he was still alive. Then, in the twelfth year of his reign, Alexander died. After that, his officers assumed power in the kingdom, each in his own territory. They all put on royal crowns after his death, as did their heirs who succeeded them for many years, inflicting great evils on the world.
- Twelfth year: 334 B.C.
| General | The Region Taken | Modern Geographical Area |
|---|---|---|
| Ptolemy | Egypt and northern Africa | Egypt, Libya, and Northern Africa |
| Seleucus | Assyria, Mesopotamia and Persia | Lebanon, Syria and Iraq, Iran |
| Lysimachus | Thrace and Asia Minor | Turkey and southern Russia |
| Cassander | Greece and Macedonia | Greece, Bulgaria, and Romania |
