Ancient Greek Life
Greek Life
But how, you will ask, did the ancient Greeks have time to look after their families and their business if they were forever running to the marketplace to discuss affairs of state? In this chapter I shall tell you.
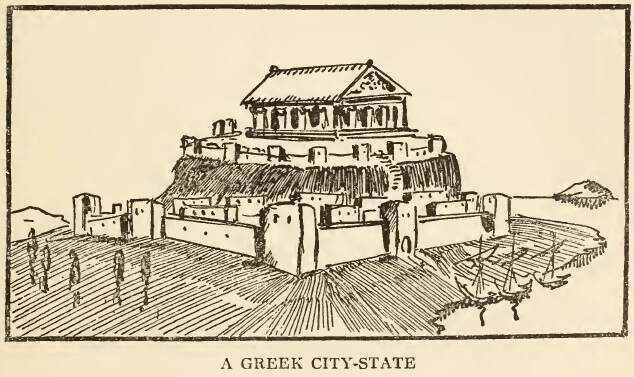
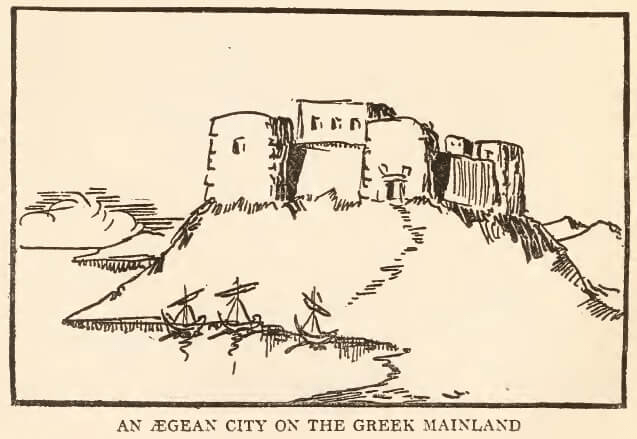
In all matters of government, the Greek democracy recognized only one class of citizens—the freemen. Every Greek city was composed of a small number of free born citizens, a large number of slaves and a sprinkling of foreigners.
The Greek city, therefore, whenever it was not ruled by a king or a tyrant, was run by and for the freemen, and this would not have been possible without a large army of slaves who outnumbered the free citizens at the rate of six or five to one and who performed those tasks to which we modern people must devote most of our time and energy if we wish to provide for our families and pay the rent of our apartments. The slaves did all the cooking and baking and candlestick making of the entire city. They were the tailors and the carpenters and the jewelers and the school-teachers and the bookkeepers and they tended the store and looked after the factory while the master went to the public meeting to discuss questions of war and peace or visited the theater to see the latest play of Aeschylus or hear a discussion of the revolutionary ideas of Euripides, who had dared to express certain doubts upon the omnipotence of the great god Zeus.
Indeed, ancient Athens resembled a modern club. All the freeborn citizens were hereditary members and all the slaves were hereditary servants, and waited upon the needs of their masters.
The slaves also took care of those tasks which nowadays are performed by the business people and the professional people. As for those household duties which take up so much of the time of your parents, the Greeks, who understood the value of leisure, had reduced such duties to the smallest possible minimum by living amidst surroundings of extreme simplicity.
To begin with, their homes were very plain. Even the rich nobles spent their lives in a sort of adobe barn, which lacked all the comforts which a modern workers expects as their natural right. A Greek home consisted of four walls and a roof. There was a door which led into the street but there were no windows. The kitchen, the living rooms and the sleeping quarters were built around an open courtyard in which there was a small fountain, or a statue and a few plants to make it look bright. Within this courtyard the family lived when it did not rain or when it was not too cold. In one corner of the yard the cook (who was a slave) prepared the meal and in another corner, the teacher (who was also a slave) taught the children the alpha beta gamma and the tables of multiplication and in still another corner the lady of the house, who rarely left her domain (since in those ancient times it was not considered good form for a married woman to be seen on the street too often) was repairing her husband’s coat with her seamstresses (who were slaves,) and in the little office, right off the door, the master was inspecting the accounts which the overseer of his farm (who was a slave) had just brought to him.
When dinner was ready the family came together but the meal was a very simple one and did not take much time. The Greeks seem to have regarded eating as an unavoidable evil and not a pastime, which kills many dreary hours and eventually kills many dreary people. They lived on bread and on wine, with a little meat and some green vegetables. They drank water only when nothing else was available because they did not think it very healthy. They loved to call on each other for dinner, but our idea of a festive meal, where everybody is supposed to eat much more than is good for him, would have disgusted them. They came together at the table for the purpose of a good talk and a good glass of wine and water, but as they were moderate people they despised those who drank too much.
The same simplicity which prevailed in the dining room also dominated their choice of clothes. They liked to be clean and well groomed, to have their hair and beards neatly cut, to feel their bodies strong with the exercise and the swimming of the gymnasium, but they never followed the Asiatic fashion which prescribed loud colors and strange patterns. They wore a long white coat and they managed to look as smart as a modern Italian officer in his long blue cape.
They loved to wear ornaments but they thought it very vulgar to display their wealth (or their wives) in public and whenever the women left their home they were as inconspicuous as possible.
In short, the story of Greek life is a story not only of moderation but also of simplicity. “Things,” chairs and tables and books and houses and carriages, are apt to take up a great deal of their owner’s time. In the end they invariably make him their slave and their hours are spent looking after their wants, keeping them polished and brushed and painted. The Greeks, before everything else, wanted to be “free,” both in mind and in body. That they might maintain their liberty, and be truly free in spirit, they reduced their daily needs to the lowest possible point.




 This sign however was too cumbersome and after a short while when the meaning of “heaven” was added to that of star the picture was simplified which made it even more of a puzzle.
This sign however was too cumbersome and after a short while when the meaning of “heaven” was added to that of star the picture was simplified which made it even more of a puzzle. In the same way an ox changed from
In the same way an ox changed from into
into and a fish changed from
and a fish changed from into
into The sun was originally a plain circle
The sun was originally a plain circle and became
and became If we were using the Sumerian script today we would make an
If we were using the Sumerian script today we would make an look like
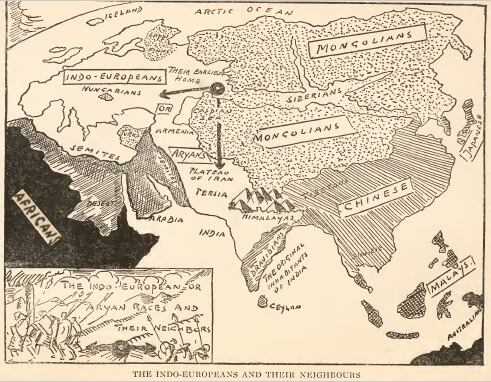
look like This system of writing down our ideas looks rather complicated but for more than thirty centuries it was used by the Sumerians and the Babylonians and the Assyrians and the Persians and all the different races which forced their way into the fertile valley. The story of Mesopotamia is one of endless warfare and conquest. First the Sumerians came from the North. They were a Caucasian people who had lived in the mountains. They had been accustomed to worship their gods on the tops of hills. After they had entered the plain, they constructed artificial little hills on top of which they built their altars. They did not know how to build stairs, and they therefore surrounded their towers with sloping galleries. Our engineers have borrowed this idea, as you may see in our big railroad stations where ascending galleries lead from one floor to another. We may have borrowed other ideas from the Sumerians, but we do not know it.
This system of writing down our ideas looks rather complicated but for more than thirty centuries it was used by the Sumerians and the Babylonians and the Assyrians and the Persians and all the different races which forced their way into the fertile valley. The story of Mesopotamia is one of endless warfare and conquest. First the Sumerians came from the North. They were a Caucasian people who had lived in the mountains. They had been accustomed to worship their gods on the tops of hills. After they had entered the plain, they constructed artificial little hills on top of which they built their altars. They did not know how to build stairs, and they therefore surrounded their towers with sloping galleries. Our engineers have borrowed this idea, as you may see in our big railroad stations where ascending galleries lead from one floor to another. We may have borrowed other ideas from the Sumerians, but we do not know it. The Sumerians were entirely absorbed by those races that entered the fertile valley at a later date. Their towers however still stand amidst the ruins of Mesopotamia. The Jews saw them when they went into exile in the land of Babylon and they called them towers of Babillli, or towers of Babel. In the fortieth century before our era, the Sumerians had entered Mesopotamia. They were soon afterwards overpowered by the Akkadians, one of the many tribes from the desert of Arabia who speak a common dialect and who are known as the “Semites,” because in the olden days people believed them to be the direct descendants of Shem, one of the three sons of Noah. A thousand years later, the Akkadians were forced to submit to the rule of the Amorites, another Semitic desert tribe whose great King Hammurabi built himself a magnificent palace in the holy city of Babylon and who gave his people a set of laws which made the Babylonian state the best administered empire of the ancient world. Next the Hittites, whom you will also meet in the Old Testament, over-ran the Fertile Valley and destroyed whatever they could not carry away. They in turn were vanquished by the followers of the great desert god, Ashur, who called themselves Assyrians and who made the city of Nineveh the center of a vast and terrible empire which conquered all of western Asia and Egypt and gathered taxes from countless subject races until the end of the seventh century before the birth of Christ when the Chaldeans, also a Semitic tribe, re-established Babylon and made that city the most important capital of that day. Nebuchadnezzar, the best known of their Kings, encouraged the study of science, and our modern knowledge of astronomy and mathematics is all based upon certain first principles which were discovered by the Chaldeans. In the year 538 B.C. a crude tribe of Persian shepherds invaded this old land and overthrew the empire of the Chaldeans. Two hundred years later, they in turn were overthrown by Alexander the Great, who turned the Fertile Valley, the old melting-pot of so many Semitic races, into a Greek province. Next came the Romans and after the Romans, the Turks, and Mesopotamia, the second center of the world’s civilization, became a vast wilderness where huge mounds of earth told a story of ancient glory.
The Sumerians were entirely absorbed by those races that entered the fertile valley at a later date. Their towers however still stand amidst the ruins of Mesopotamia. The Jews saw them when they went into exile in the land of Babylon and they called them towers of Babillli, or towers of Babel. In the fortieth century before our era, the Sumerians had entered Mesopotamia. They were soon afterwards overpowered by the Akkadians, one of the many tribes from the desert of Arabia who speak a common dialect and who are known as the “Semites,” because in the olden days people believed them to be the direct descendants of Shem, one of the three sons of Noah. A thousand years later, the Akkadians were forced to submit to the rule of the Amorites, another Semitic desert tribe whose great King Hammurabi built himself a magnificent palace in the holy city of Babylon and who gave his people a set of laws which made the Babylonian state the best administered empire of the ancient world. Next the Hittites, whom you will also meet in the Old Testament, over-ran the Fertile Valley and destroyed whatever they could not carry away. They in turn were vanquished by the followers of the great desert god, Ashur, who called themselves Assyrians and who made the city of Nineveh the center of a vast and terrible empire which conquered all of western Asia and Egypt and gathered taxes from countless subject races until the end of the seventh century before the birth of Christ when the Chaldeans, also a Semitic tribe, re-established Babylon and made that city the most important capital of that day. Nebuchadnezzar, the best known of their Kings, encouraged the study of science, and our modern knowledge of astronomy and mathematics is all based upon certain first principles which were discovered by the Chaldeans. In the year 538 B.C. a crude tribe of Persian shepherds invaded this old land and overthrew the empire of the Chaldeans. Two hundred years later, they in turn were overthrown by Alexander the Great, who turned the Fertile Valley, the old melting-pot of so many Semitic races, into a Greek province. Next came the Romans and after the Romans, the Turks, and Mesopotamia, the second center of the world’s civilization, became a vast wilderness where huge mounds of earth told a story of ancient glory.