Chapter 2: Animal Language
It happened one day that the Doctor was sitting in his kitchen talking with the Cat’s-meat-Man who had come to see him with a stomach-ache.
“Why don’t you give up being a people’s doctor, and be an animal-doctor?” asked the Cat’s-meat-Man.
The parrot, Polynesia, was sitting in the window looking out at the rain and singing a sailor-song to herself. She stopped singing and started to listen.
“You see, Doctor,” the Cat’s-meat-Man went on, “you know all about animals-much more than what these here vets do. That book you wrote-about cats, why, it’s wonderful! I can’t read or write myself-or maybe I’d write some books. But my wife, Theodosia, she’s a scholar, she is. And she read your book to me. Well, it’s wonderful-that’s all can be said-wonderful. You might have been a cat yourself. You know the way they think. And listen: you can make a lot of money doctoring animals. Do you know that? You see, I’d send all the old women who had sick cats or dogs to you. And if they didn’t get sick fast enough, I could put something in the meat I sell ’em to make ’em sick, see?”
“Oh, no,” said the Doctor quickly. “You mustn’t do that. That wouldn’t be right.”
“Oh, I didn’t mean real sick,” answered the Cat’s-meat-Man. “Just a little something to make them droopy-like was what I had reference to. But as you say, maybe it ain’t quite fair on the animals. But they’ll get sick anyway, because the old women always give ’em too much to eat. And look, all the farmers round about who had lame horses and weak lambs-they’d come. Be an animal-doctor.”
When the Cat’s-meat-Man had gone the parrot flew off the window on to the Doctor’s table and said,
“That man’s got sense. That’s what you ought to do. Be an animal-doctor. Give the silly people up-if they haven’t brains enough to see you’re the best doctor in the world. Take care of animals instead-they’ll soon find it out. Be an animal-doctor.”
“Oh, there are plenty of animal-doctors,” said John Dolittle, putting the flower-pots outside on the window-sill to get the rain.
“Yes, there are plenty,” said Polynesia. “But none of them are any good at all. Now listen, Doctor, and I’ll tell you something. Did you know that animals can talk?”
“I knew that parrots can talk,” said the Doctor.
“Oh, we parrots can talk in two languages-people’s language and bird-language,” said Polynesia proudly. “If I say, ‘Polly wants a cracker,’ you understand me. But hear this: Ka-ka oi-ee, fee-fee?”
“Good Gracious!” cried the Doctor. “What does that mean?”
“That means, ‘Is the porridge hot yet?’-in bird-language.”
“My! You don’t say so!” said the Doctor. “You never talked that way to me before.”
“What would have been the good?” said Polynesia, dusting some cracker-crumbs off her left wing. “You wouldn’t have understood me if I had.”
“Tell me some more,” said the Doctor, all excited; and he rushed over to the dresser-drawer and came back with the butcher’s book and a pencil. “Now don’t go too fast-and I’ll write it down. This is interesting-very interesting-something quite new. Give me the Birds’ A.B.C. first-slowly now.”
So that was the way the Doctor came to know that animals had a language of their own and could talk to one another. And all that afternoon, while it was raining, Polynesia sat on the kitchen table giving him bird words to put down in the book.
At tea-time, when the dog, Jip, came in, the parrot said to the Doctor, “See, he’s talking to you.”
“Looks to me as though he were scratching his ear,” said the Doctor.
“But animals don’t always speak with their mouths,” said the parrot in a high voice, raising her eyebrows. “They talk with their ears, with their feet, with their tails-with everything. Sometimes they don’t want to make a noise. Do you see now the way he’s twitching up one side of his nose?”
“What’s that mean?” asked the Doctor.
“That means, ‘Can’t you see that it has stopped raining?'” Polynesia answered. “He is asking you a question. Dogs nearly always use their noses for asking questions.”
After a while, with the parrot’s help, the Doctor got to learn the language of the animals so well that he could talk to them himself and understand everything they said. Then he gave up being a people’s doctor altogether.
As soon as the Cat’s-meat-Man had told everyone that John Dolittle was going to become an animal-doctor, old ladies began to bring him their pet pugs and poodles who had eaten too much cake; and farmers came many miles to show him sick cows and sheep.
One day a plow-horse was brought to him; and the poor thing was terribly glad to find a man who could talk in horse-language.
“You know, Doctor,” said the horse, “that vet over the hill knows nothing at all. He has been treating me six weeks now-for spavins. What I need is spectacles. I am going blind in one eye. There’s no reason why horses shouldn’t wear glasses, the same as people. But that stupid man over the hill never even looked at my eyes. He kept on giving me big pills. I tried to tell him; but he couldn’t understand a word of horse-language. What I need is spectacles.”
“Of course-of course,” said the Doctor. “I’ll get you some at once.”
“I would like a pair like yours,” said the horse-“only green. They’ll keep the sun out of my eyes while I’m plowing the Fifty-Acre Field.”
“Certainly,” said the Doctor. “Green ones you shall have.”
“You know, the trouble is, Sir,” said the plow-horse as the Doctor opened the front door to let him out-“the trouble is that anybody thinks he can doctor animals-just because the animals don’t complain. As a matter of fact it takes a much cleverer man to be a really good animal-doctor than it does to be a good people’s doctor. My farmer’s boy thinks he knows all about horses. I wish you could see him-his face is so fat he looks as though he had no eyes-and he has got as much brain as a potato-bug. He tried to put a mustard-plaster on me last week.”
“Where did he put it?” asked the Doctor.
“Oh, he didn’t put it anywhere-on me,” said the horse. “He only tried to. I kicked him into the duck-pond.”
“Well, well!” said the Doctor.
“I’m a pretty quiet creature as a rule,” said the horse-“very patient with people-don’t make much fuss. But it was bad enough to have that vet giving me the wrong medicine. And when that red-faced booby started to monkey with me, I just couldn’t bear it anymore.”
“Did you hurt the boy much?” asked the Doctor.
“Oh, no,” said the horse. “I kicked him in the right place. The vet’s looking after him now. When will my glasses be ready?”
“I’ll have them for you next week,” said the Doctor. “Come in again Tuesday-Good morning!”
Then John Dolittle got a fine, big pair of green spectacles; and the plow-horse stopped going blind in one eye and could see as well as ever.
And soon it became a common sight to see farm-animals wearing glasses in the country round Puddleby; and a blind horse was a thing unknown.
And so it was with all the other animals that were brought to him. As soon as they found that he could talk their language, they told him where the pain was and how they felt, and of course it was easy for him to cure them.
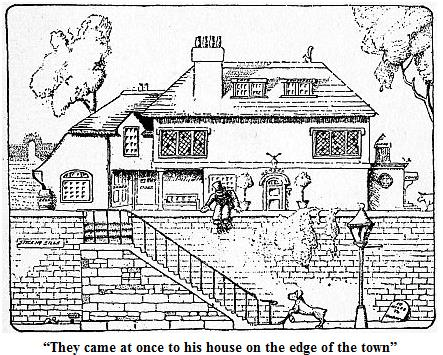
Now all these animals went back and told their brothers and friends that there was a doctor in the little house with the big garden who really was a doctor. And whenever any creatures got sick-not only horses and cows and dogs-but all the little things of the fields, like harvest-mice and water-voles, badgers and bats, they came at once to his house on the edge of the town, so that his big garden was nearly always crowded with animals trying to get in to see him.
There were so many that came that he had to have special doors made for the different kinds. He wrote “HORSES” over the front door, “COWS” over the side door, and “SHEEP” on the kitchen door. Each kind of animal had a separate door-even the mice had a tiny tunnel made for them into the cellar, where they waited patiently in rows for the Doctor to come round to them.
And so, in a few years’ time, every living thing for miles and miles got to know about John Dolittle, M.D. And the birds who flew to other countries in the winter told the animals in foreign lands of the wonderful doctor of Puddleby-on-the-Marsh, who could understand their talk and help them in their troubles. In this way he became famous among the animals-all over the world-better known even than he had been among the folks of the West Country, And he was happy and liked his life very much.
One afternoon when the Doctor was busy writing in a book, Polynesia sat in the window-as she nearly always did-looking out at the leaves blowing about in the garden. Presently she laughed aloud.
“What is it, Polynesia?” asked the Doctor, looking up from his book.
“I was just thinking,” said the parrot; and she went on looking at the leaves.
“What were you thinking?”
“I was thinking about people,” said Polynesia. “People make me sick. They think they’re so wonderful. The world has been going on now for thousands of years, hasn’t it? And the only thing in animal-language that people have learned to understand is that when a dog wags his tail he means ‘I’m glad!’-It’s funny, isn’t it? You are the very first man to talk like us. Oh, sometimes people annoy me dreadfully-such airs they put on-talking about ‘the dumb animals.’ Dumb!-Huh! Why I knew a macaw once who could say ‘Good morning!’ in seven different ways without once opening his mouth. He could talk every language-and Greek. An old professor with a gray beard bought him. But he didn’t stay. He said the old man didn’t talk Greek right, and he couldn’t stand listening to him teach the language wrong. I often wonder what’s become of him. That bird knew more geography than people will ever know.-People, Golly! I suppose if people ever learn to fly-like any common hedge-sparrow-we shall never hear the end of it!”
“You’re a wise old bird,” said the Doctor. “How old are you really? I know that parrots and elephants sometimes live to be very, very old.”
“I can never be quite sure of my age,” said Polynesia. “It’s either a hundred and eighty-three or a hundred and eighty-two. But I know that when I first came here from Africa, King Charles was still hiding in the oak-tree-because I saw him. He looked scared to death.”